Treating This Common Skin Condition
Although melasma is a lesser known skin condition, it is actually quite common. Often brought on by sun exposure or out-of-balance hormones, it is much more prevalent in women than men and frequently accompanies pregnancy. Read on to find out more about this surprisingly standard skin condition including how to spot it and how to treat it.
What is it?
Melasma is a form of hyperpigmentation (darkening of the skin) that is associated with sun exposure and can also be triggered by hormones. It predominantly affects women – in fact, melasma occurs in pregnant women so regularly that it is sometimes referred to as “the mask of pregnancy.”
This pigmentation disorder does not pose any physical harm. However, it is a skin condition that occurs most often on the face, and many patients are uncomfortable with the change in appearance. Fortunately, treatment is rather simple and noninvasive.
What are the signs?


Splotchy patches of darker skin will appear, often on the face. Usually developing across the forehead, cheeks, bridge of the nose, and upper lip, these patches range from brown to gray in color. Patches can also appear on other areas of the body that are routinely exposed to sunlight, like the forearms and neck – however, this happens much less frequently.
What are the causes?
Hormones
Melasma is frequently developed during pregnancy or periods of hormone fluctuation. Birth control pills and hormone replacement therapy can also cause this hyperpigmentation to occur.
Sun exposure
After melasma fades, even just a small amount of ultraviolet light can stimulate the pigment-forming cells and cause the discoloration to return. For this reason, melasma is often a recurring condition, and sun protection is key to keeping discoloration at bay.
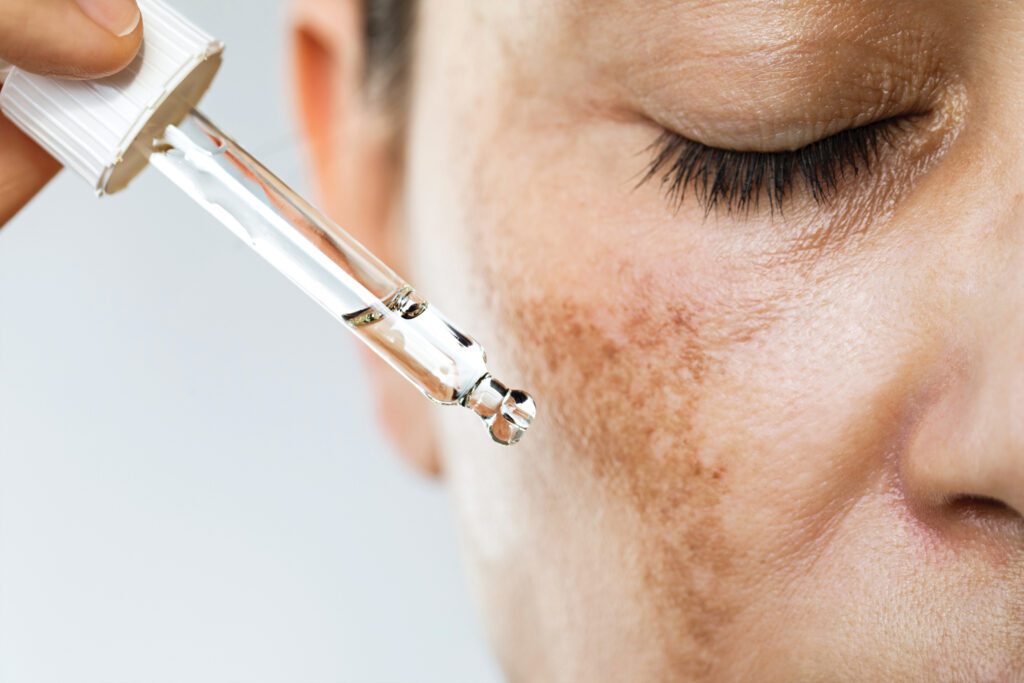


Products
Skin irritation can cause melasma to return or worsen. It’s important to be careful when changing products, and always check with your doctor before attempting to treat the condition.
How can it be treated or prevented?
Melasma is often a chronic issue. It can be present for the rest of your life, or it may disappear when hormone levels return to normal.
Because sun exposure is the most common way to cause recurrence, the best prevention is to wear sun protection daily. Sunscreen of SPF 30 or higher should be applied to the face, neck, and other exposed areas each morning, reapplying as needed throughout the day.
Doctors often treat melasma with topical medications. Creams, lotions, gels, or liquids come with different active ingredients, meant to enhance treatment intensity as needed.
Hydroquinone
This is the active ingredient in the typical first line of treatment for melasma. It’s sold in a variety of forms, including creams, gels, and liquids. These products also contain differing amounts of the active ingredient. Some of the lower concentrations of hydroquinone can be purchased at the pharmacy, while stronger concentrations should be prescribed by your dermatologist.
Tretinoin and corticosteroids
These are additional active ingredients that may be prescribed separately to enhance the skin-lightening process, or they may be combined with hydroquinone in what is often called a triple cream.
Your doctor may prescribe additional medications for skin lightening, including azelaic acid and kojic acid.
If topical medications aren’t helping, a procedure could be the answer. In-office methods include chemical peels, microdermabrasion, dermabrasion, laser treatment, and light-based procedures. Because each patient’s unique skin composition must be taken into consideration, it is imperative to have these procedures performed by medical professionals that can tailor the treatment to your specific needs.
Melasma is known to be stubborn, often requiring several months of treatment, and it may never go away completely. After treatment, if your melasma has been lightened, continue to protect your skin from UV exposure. If you experience darkening skin or irritation, consult your doctor as soon as possible. A few tips to carry with you as you work to prevent or maintain melasma: Apply sunscreen daily, wear a brimmed hat and glasses when outside, avoid waxing or other harsh skin treatments, and choose gentle skin care products.

